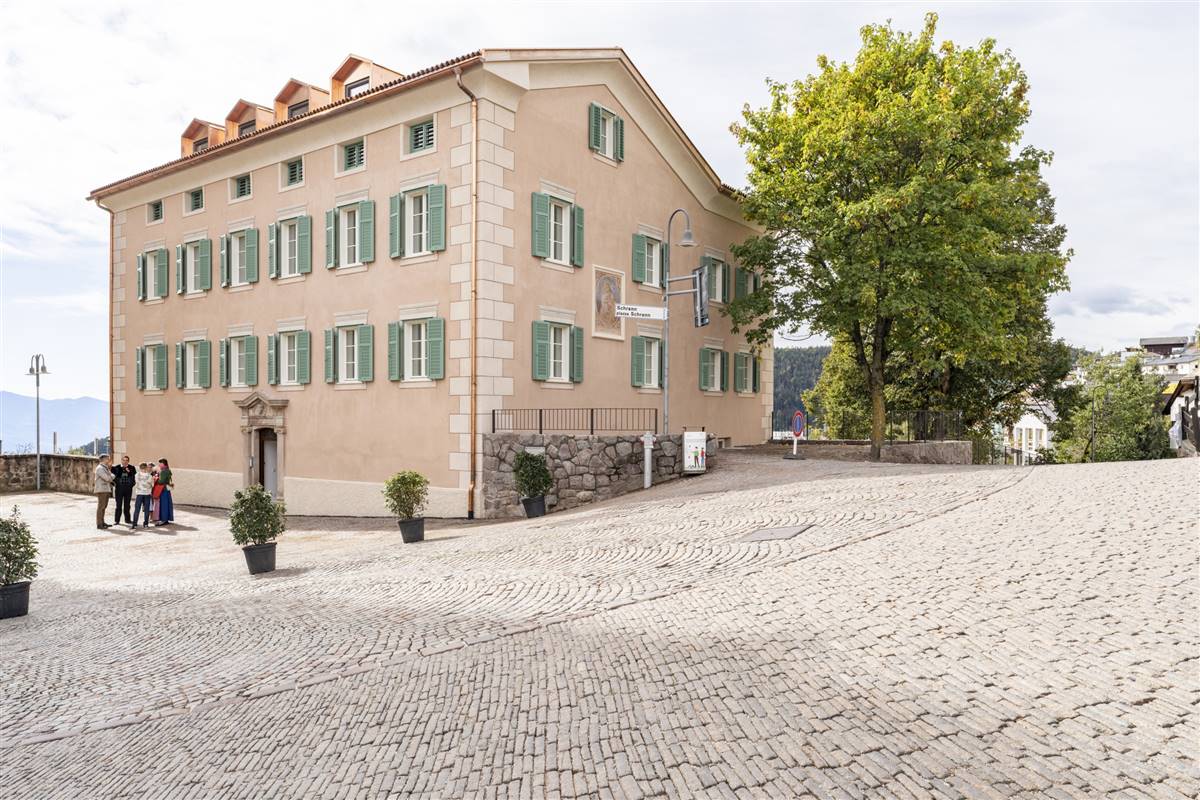
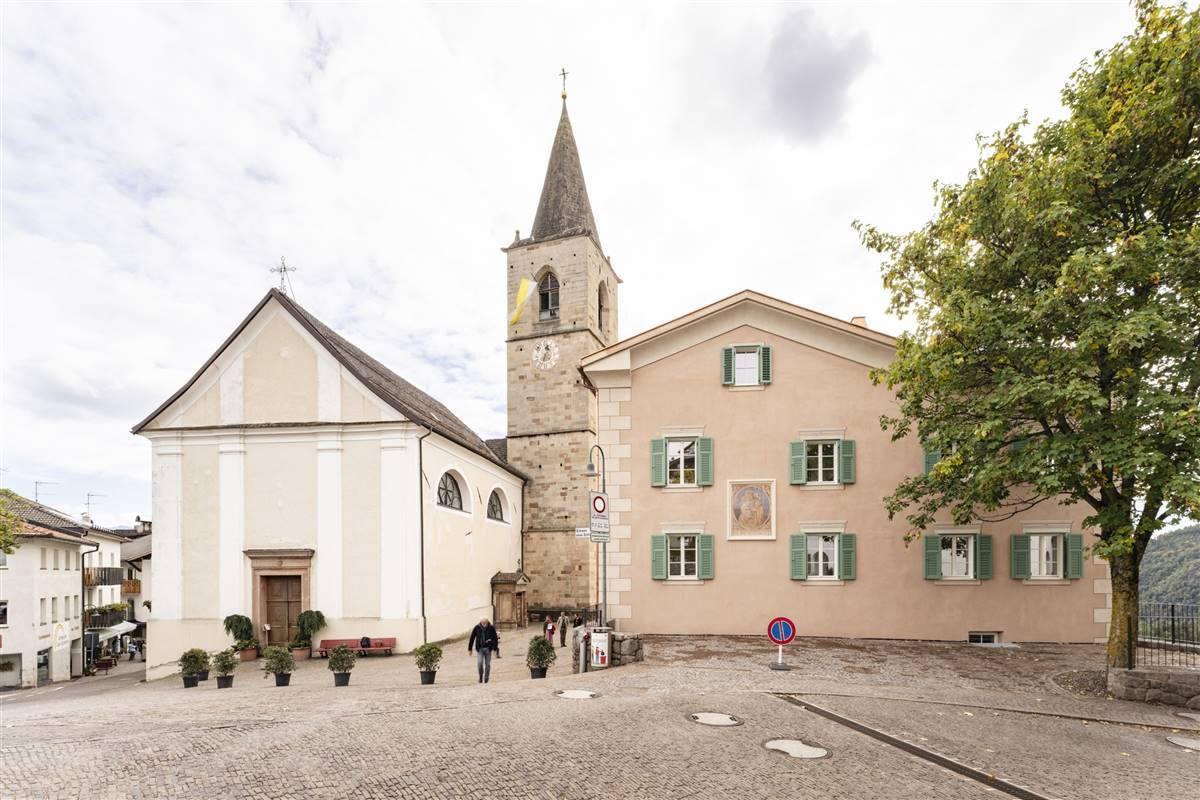
Widum in Jenesien
via Paese
39050
San Genesio, Italien
Besitzer
Bewohner
Ansprechpartner
Other Information
upon prior request

73 kWh/m2.y
Klimazone F
Höhe über dem Meer 1000 m ü.d.M.
Heizgradtage 4073
Kühlgradtage 0
Ensembleschutz:
Ja
Stufe der Unterschutzstellung:
Historical City Center
Letzte Sanierung:
2021
Gebäudebelegung:
Permanently occupied
Gebäudetyp:
Detached house
Anzahl der Stockwerke:
4
Keller ja/nein:
Ja
Anzahl der beheizten Stockwerke:
0
Bruttogeschossfläche [m²]:
0,0
Thermische Gebäudehülle [m²]:
1228,0
Volumen [m³]:
2510,0
NGF Berechnungsmethode:
Useful area (it)
Außen:
Rendered
Innen:
Plastered (on hard)
Dach:
Pitched roof
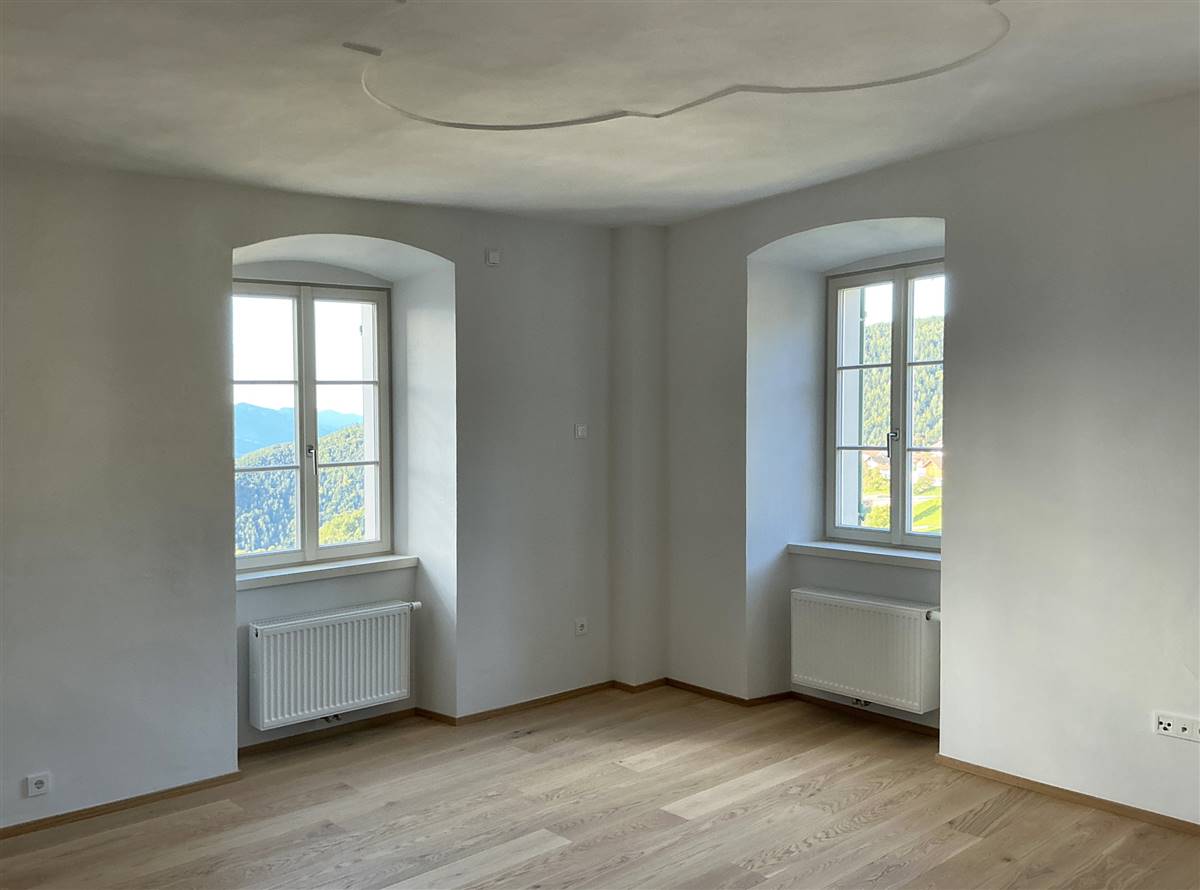
RENOVIERUNGS-PROZESS
Architektur
BESCHREIBUNG
Erhaltungszustand
DENKMALWERT
Ziel der Sanierung
Hygrothermische Bewertung Glaser (Relazione ex L.10)
SANIERUNGS-LÖSUNGEN
Außenwände
Stone masonry
The intervention involved installing a variable-thickness internal insulating plaster based on perlite, applied to the stone masonry to improve thermal performance without altering the historic building’s exterior appearance. This solution reduced the wall U-value from 1.53 to 0.63 W/m²K while remaining compatible with conservation constraints.
The intervention is conservation-compatible because it is applied from the inside, avoiding any changes to façades and volume and preserving the building’s historic appearance. Moreover, using a mineral perlite-based insulating plaster is consistent with traditional substrates and supports a discreet, potentially reversible solution.
50 mm
600 mm
50 mm
50mm
600 mm
60 mm
Fenster
Window
The original historic window was retained and integrated into a “double-layer” solution: traditional external shutters remain in place, while a secondary timber-framed inner window was added on the inside to improve performance without changing the exterior appearance.
The external shutters were replaced and redone in the same style, the original window was retained, and another internal window frame was added, featuring modern performance and a subtle look.
| Fenstertyp Bestand | Double window |
| Verglasungsart Bestand | Single |
| Verschattung Bestand | Outer shutter |
| Ungefähres Einbaujahr | 2021 |
| Neuer Fenstertyp | Casement window |
| Verglasungsart des neuen Fensters | Double |
| Verschattung des neuen Fensters | Outer shutter |
| Neuer Energiedurchlassgrad g [-] | 0,05 |
Weitere Maßnahmen
DACH
ERDGESCHOSS
The roof was thermally insulated by installing 19 cm of wood fiber insulation panels, significantly improving the energy performance of the building envelope while ensuring breathability and compatibility with the existing structure.
The roof intervention involved a full reconstruction of the roof, while keeping the original geometry and volume unchanged. Although the materials and build-up were replaced, the solution remains conservation-compatible because it does not alter façades or the roof silhouette and does not change the building’s external appearance; performance is upgraded while preserving architectural identity and the relationship with the historic context.
20 mm
25 mm
200 mm
25 mm
60 mm
12 mm
18 mm
160 mm
35 mm
Before the intervention, the ground-contact floor slab featured an insulating layer consisting of a 12 cm thick XPS (extruded polystyrene) panel, placed beneath the structural slab. The existing configuration provided a level of thermal insulation that was not fully optimized with respect to current energy efficiency requirements.
The intervention is compatible with building conservation requirements, as it does not alter load-bearing structures nor introduce visible changes to the existing architectural elements.
200 mm
60 mm
20 mm
80 mm
120 mm
10 mm
50 mm
15 mm
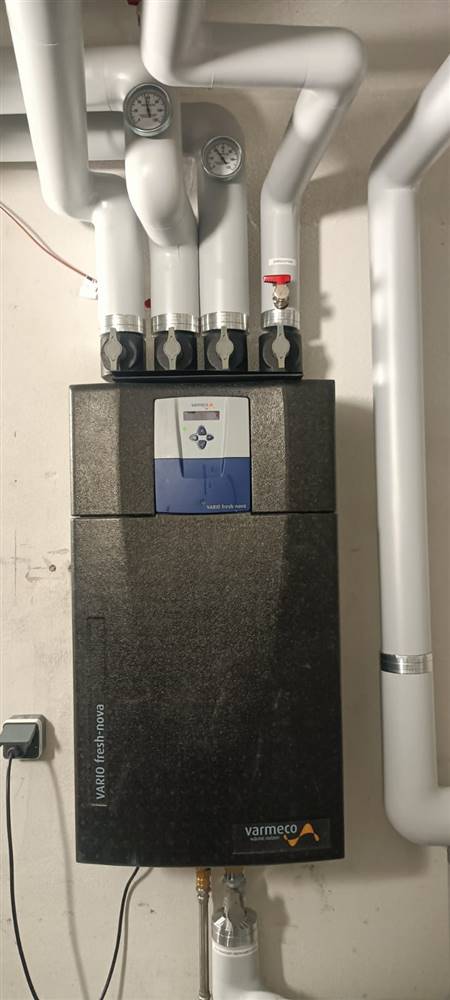
HVAC
HEIZUNG
BRAUCHWARMWASSER
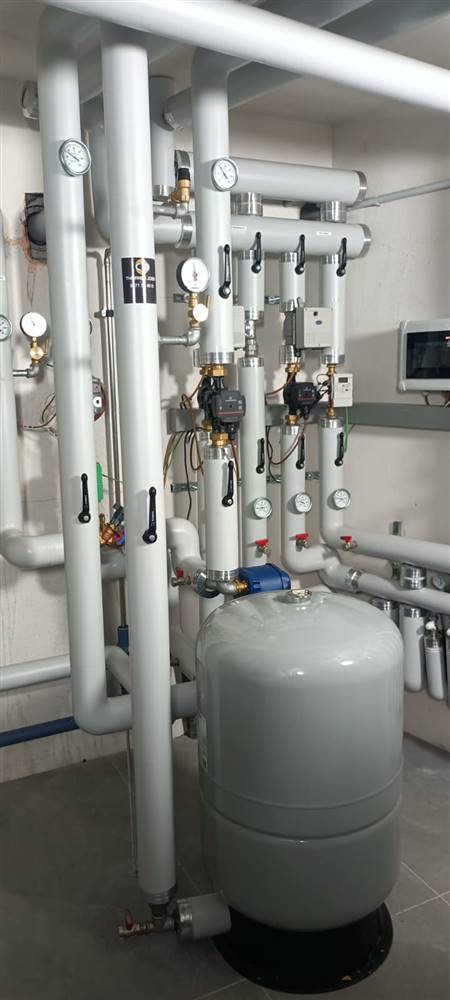
As part of the building energy renovation, the heating system was converted to district heating, allowing the building to be integrated into a centralized heat production and distribution network.
All technical systems are located in a semi-basement technical room, with no interference with architectural elements and no impact on the building’s aesthetic appearance.
| Heizungssystem nach Sanierung | |
|---|---|
| Art der Heizung | District Heating |
| Brennstoff | District Heating |
| Wärmeverteilung | Radiators |
| Nennleistung | 40 kW |
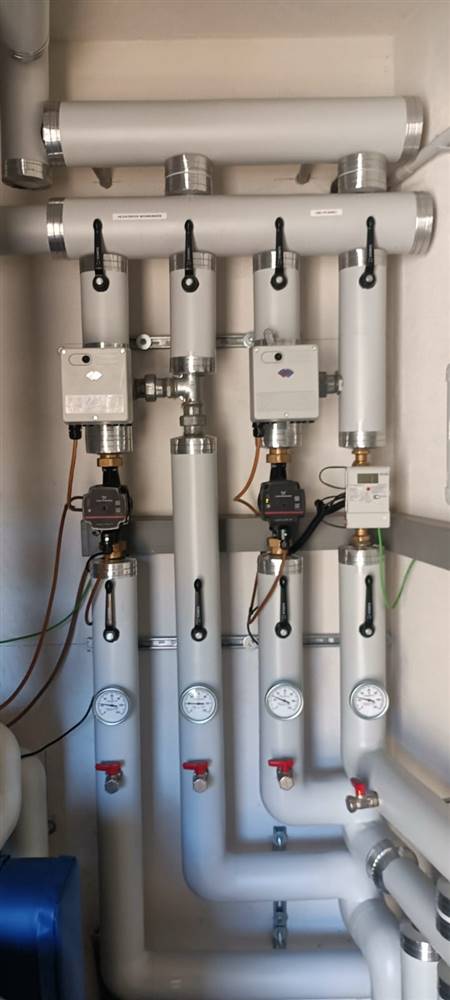
As part of the building energy renovation, the heating system was converted to district heating, allowing the building to be integrated into a centralized heat production and distribution network.
All technical systems are located in a semi-basement technical room, with no interference with architectural elements and no impact on the building’s aesthetic appearance.
| Brauchwarmwasserbereitung nach Sanierung | |
|---|---|
| Typ | District Heating |
| Brauchwasserspeicher | Nein |
| Wärmerückgewinnung aus Brauchwasser | Nein |
Energieeffizienz
Freiwillige Zertifikate Nein
Primärenergie 73 kWh/m2.y
Primärenergie
Berechnungsmethode CasaClima
Energieverbrauch incl Brauchwarmwasser Nein
Energieverbrauch nach Sanierung 73 kWh/m2.y
Kosten
approx. 1.800.000 euro
€ (total)
Nein





.jpg)




